
With the rapid development of the solar energy industry, a large number of solar panels are gradually reaching the end of their service life. Recycling these decommissioned panels not only helps recover valuable raw materials but also effectively reduces the burden on landfills.

Statistics show that by 2030, the cumulative value of recyclable materials from discarded solar panels worldwide is expected to reach approximately USD 450 million, equivalent to the material cost for manufacturing around 60 million new panels. Therefore, promoting the recycling and reuse of solar panels is not only economically valuable but also environmentally significant.
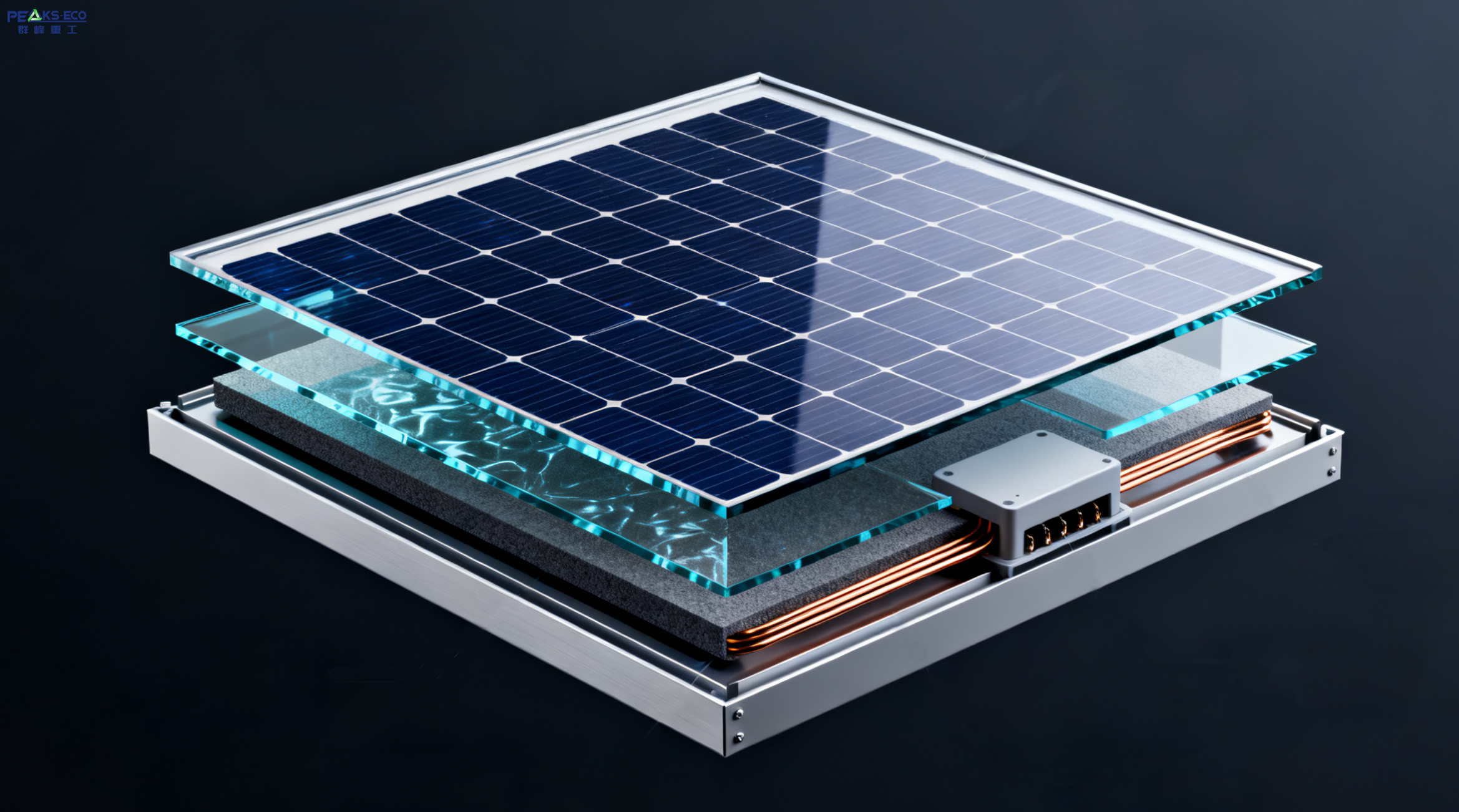
The mainstream solar panels in the market today are crystalline silicon panels. Their main components include:
Aluminum frame
Glass
Copper wires
Polymer layers and backsheet
Silicon solar cells
Plastic junction box
Among these, glass accounts for about 75% of the total panel weight. Although polymer layers provide sealing and weather protection, they are usually difficult to separate because high temperatures are required to loosen the adhesives, posing challenges for recycling and disassembly.
Many components of solar panels have recycling value:
Easily recyclable materials: glass, aluminum frame, copper wires, and plastic junction boxes, with glass recycling already forming a mature industry chain.
High-value but difficult-to-recycle materials: metals such as silver and copper, which are present in low concentrations and require complex recycling processes.
Materials with environmental risks: toxic metals such as lead and cadmium, which must be properly handled.
Critical materials: some panels may also contain aluminum, tin, tellurium, antimony, gallium, and indium, which have recycling potential.
Additionally, components in the solar power system, such as inverters, mounts, and backup batteries, can be processed through e-waste, metal scrap, and battery recycling channels, respectively.
A comprehensive solar panel recycling system aims to maximize material recovery. Common recycling steps include:
Dismantling frames and junction boxes
Separating glass from silicon wafers using thermal, mechanical, or chemical methods
Applying chemical and electronic techniques to separate and purify silicon cells and metals such as silver, tin, lead, and copper

Currently, solar panel recycling is still an emerging industry, and related technologies are continually evolving. Researchers are developing economically feasible commercial recycling solutions to improve material recovery rates. Existing recycling often relies on the glass, metal, and electronic waste processing industries, using methods such as crushing, shredding, and grinding. These processes allow the recovery of glass, aluminum, and copper, while silicon cells may sometimes be incinerated.
In addition to recycling, solar panels can also be directly reused or refurbished, preventing them from entering landfills. Reusable panels can continue to function in different settings, such as for electric bicycles or car charging stations, and off-grid power supply in remote areas.
With continuous technological advancement and increasingly mature recycling systems, the recycling and reuse of solar panels have become an indispensable part of the green energy supply chain. This is not only crucial for resource circulation and economic benefits but also a key step toward achieving a sustainable, full lifecycle for the solar industry. Through proactive policy guidance, technological innovation, and market development, each decommissioned solar panel can be transformed into a valuable resource for building a clean future, truly achieving a complete lifecycle from a “green start” to a “green end.”