With the rapid growth of the new energy industry, lithium battery recycling has become a global focus. From electric vehicles to energy storage systems, the surge in retired batteries presents both environmental challenges and valuable resource opportunities. As a result, a complete industrial chain covering the upstream, midstream, and downstream sectors has emerged.
The recycling process begins with the collection and pre-treatment of waste lithium batteries, including sorting, discharging, and dismantling. Different types—such as ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries—require tailored approaches, with the key objective being safety and efficiency.
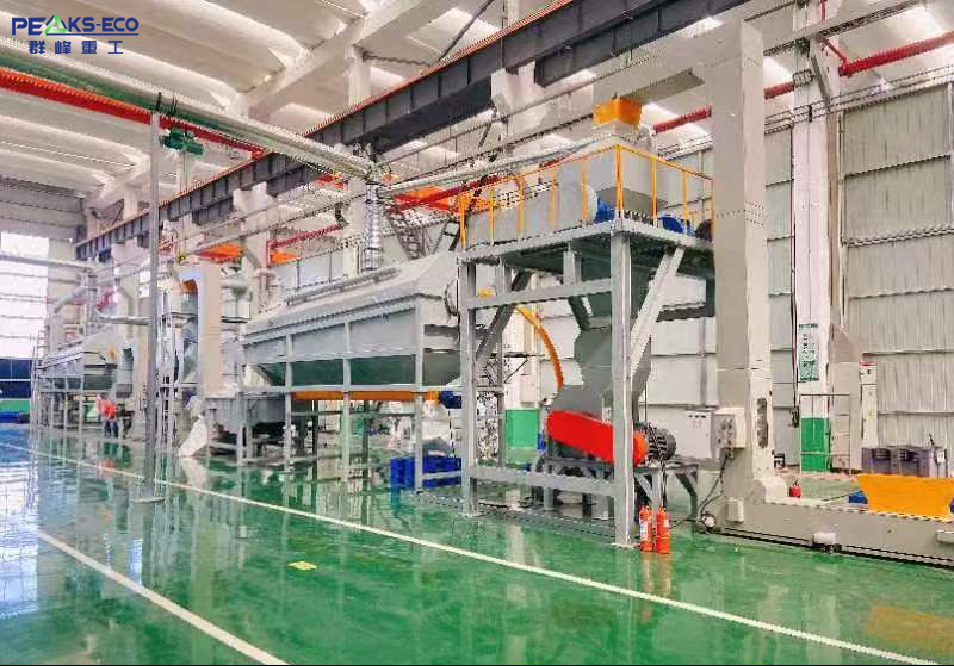

In Asia, upstream activities are mainly handled by local recycling companies and the recycling divisions of major battery manufacturers. These entities often establish stable material supply channels by signing long-term agreements with automakers and battery producers.
At this stage, cost control and safety management are critical. Given the complex composition and potential hazards of batteries, reducing dismantling risks and improving automation levels have become key factors for enhancing operational efficiency.
The midstream sector is where the real value of recycling is realized. This stage involves crushing, separation, and extraction of “black powder.”
“Black powder” refers to the mixed powder obtained from crushed cathode materials. It is rich in valuable metals such as nickel, cobalt, manganese, and lithium—key raw materials for reuse. Its price fluctuates with metal market trends. For example, in 2025, the price of ternary 523 cathode black powder ranged from RMB 71,000 to 75,000 per ton, while lithium iron phosphate black powder was priced between RMB 10,000 and 15,000 per ton. The difference mainly results from variations in metal content and extraction difficulty.
Two primary metallurgical processes dominate the industry: pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy. Pyrometallurgy involves high-temperature smelting to extract metals—simple in process but energy-intensive. Hydrometallurgy, by contrast, uses chemical leaching for higher recovery rates, though at higher cost. Companies generally choose the most suitable route based on their operational capabilities.
We are currently developing a sustainable lithium-ion battery recycling solution aimed at recovering materials from both production scrap and end-of-life batteries.
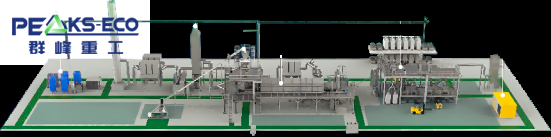
Our process covers consumer electronics batteries (such as those with lithium cobalt oxide [LCO] cathodes) as well as high-nickel batteries used in electric vehicles and stationary energy storage (such as lithium nickel manganese cobalt [NMC] cathodes). The system efficiently recovers valuable materials including cobalt, nickel, lithium, copper, iron, aluminum, carbon, plastic, and manganese. These recovered materials are then converted into marketable products that meet the quality requirements of the battery supply chain, achieving true resource circularity.
In terms of technology, PEAKS-ECO’s sustainable hydrometallurgical process provides a highly safe recycling pathway. Operating at ambient temperature, it uses a closed-loop liquid solvent system to extract metals and return high-purity chemical compounds to the battery manufacturing cycle. In comparison, the commonly used pyrometallurgical method—with its high energy consumption and emissions—is increasingly regarded as an outdated approach. Hydrometallurgy, as an emerging “sunrise” technology, is poised to play a vital role in reducing the carbon footprint of the lithium battery industry.
After refining, the valuable metals extracted from black powder are transformed into battery-grade chemicals such as cobalt sulfate, nickel sulfate, and lithium carbonate. These materials are then reintegrated into the battery production process—completing the transformation from “waste” to “resource.”
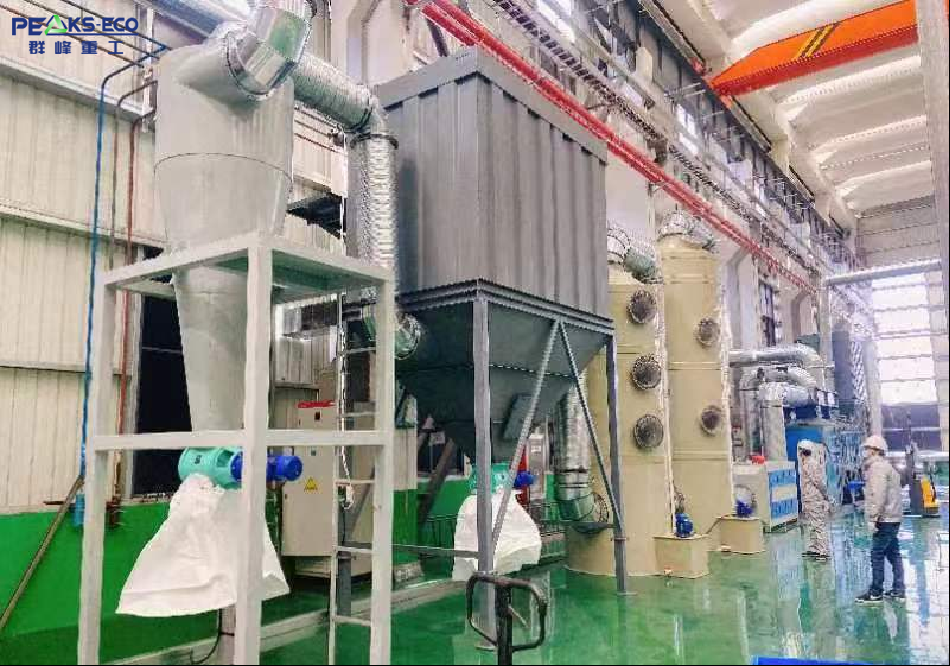

Downstream enterprises maintain close cooperation with upstream material processors and battery manufacturers. By 2025, the recycling capacity in Asian markets (excluding China) has grown rapidly. Countries such as Malaysia, Thailand, and Indonesia are developing local recycling systems and emerging as regional “recycling and processing hubs.”
Driven by global carbon neutrality goals, government policies are providing strong support for lithium battery recycling. The European Union has introduced mandatory recycling targets, Japan and South Korea are implementing Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) systems, and Southeast Asian nations are accelerating legislative frameworks—all contributing to the steady advancement of the industry.
From a competitive perspective, the global lithium battery recycling market is becoming increasingly consolidated. Technologically advanced enterprises are securing leading positions through process optimization and economies of scale, while emerging markets are demonstrating strong growth potential. As technologies continue to evolve and industrial collaboration deepens, lithium battery recycling will remain a crucial pillar supporting the sustainable development of the new energy sector